Efficient sucrose-derived mesoporous carbon sphere electrodes with enhanced hydrophilicity for water capacitive deionization at low cell voltages
Abstract
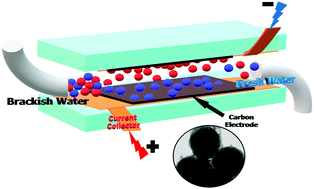
Capacitive deionization is emerging as an energy-efficient technology for water desalination and research is continuing to find better electrode materials in order to achieve favorable properties and good desalination behavior. In this study, mesoporous carbon spheres (MCSs) were synthesized employing the hard template approach using mesoporous silica nanospheres (MSNs) with a narrow pore size distribution as the hard template and sucrose as a low cost naturally occurring carbon source. The as-synthesized carbon/silica composites were carbonized at three different temperatures of 700, 800 and 900 °C followed by etching. The synthesized MCSs were characterized by a variety of techniques including: small and wide angle X-ray diffraction, Raman spectroscopy, nitrogen sorption studies, scanning electron microscopy, high resolution transmission electron microscopy and contact angle measurements. The electrochemical behavior of the synthesized material was studied using three techniques, namely, cyclic voltammetry, galvanostatic charge/discharge and potentiostatic electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. As a pristine carbon material, the synthesized electrodes in this study exhibited promising properties in comparison with other mesoporous carbon electrodes reported in the literature including: high specific capacitance (163.88 F g−1) at a 1 mV scan rate, superior electrical conductivity, better hydrophilicity and low charge transfer resistance. The desalination potency including the recyclability of the electrodes was evaluated and our material showed reasonable salt adsorption capacity (9.29 mg g−1), which makes the mesoporous carbon spheres (MCSs) in this work stand out as a potential candidate for CDI based water desalination.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...