Iron-catalyzed C–O bond functionalization of butyrolactam derivatives with various N-/C-nucleophiles†
Abstract
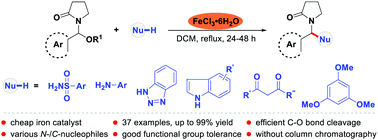
An efficient iron-catalyzed C–O bond functionalization of butyrolactam derivatives with various N-/C-nucleophiles to enable the synthesis of pharmaceutically important butyrolactam derivatives has been developed here. The versatility of the present methodology is demonstrated for direct amination and carbonation by using a variety of sulfonamides, amines, amides, indoles, and 1,3-dicarbonyl compounds under mild conditions. The reaction also showed a wide substrate scope and synthetic simplicity. Additionally, only alcohol was produced as the by-product in all cases.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...