Photophysical properties and electron transfer photochemical reactivity of substituted phthalimides†
Abstract
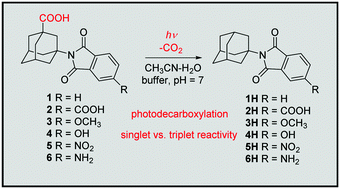
The photochemical reactivity and photophysical and electrochemical properties of a series of N-adamantylphthalimides bearing carboxylic functional groups were investigated. Upon irradiation (with or without a triplet sensitizer), the compounds undergo decarboxylation via photoinduced electron transfer (PET) from the carboxylate to the phthalimide. UV-vis and fluorescence pH titrations were used to determine pKa values for the prototropic forms, which were put in connection with the quantum yields of the reaction (ΦR). The compounds bearing electron donors OH and OCH3 at the phthalimide 4 position are fluorescent (ΦF = 0.02–0.49) and PET takes place from both singlet and triplet excited states. The estimated rate constants for PET in the singlet excited states for the methoxy- and amino-substituted phthalimides are (2.0 ± 0.1) × 109 s−1 and (3.4 ± 1.0) × 107 s−1, respectively. Laser flash photolysis (LFP) was conducted to characterize the triplet excited states, which are populated less efficiently for compounds with electron donors. The PET is reversible and the overall ΦR depends on the rates for back electron transfer, protonation of the phthalimide radical anion and decarboxylation. The plausible photochemical and photophysical pathways depend on the phthalimide substituents, which is important for the use of phthalimide derivatives in organic synthesis and photocatalysis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...