An amphiphilic BODIPY-based selective probe for parallel G4 DNA targeting via disaggregation-induced emission†
Abstract
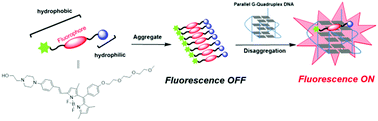
The implication of G4 DNA in biologically important roles has prompted a search for methods of selective recognition of and interaction with G4 agents. Because G4 DNA structures can adopt various topologies, attaining a specific G4 topology over other structural similarities is a challenging task given the subtle structural variations in their loops, groove widths, and flanking nucleotides. To achieve this, a new amphiphilic fluorescent probe, AB-1, has been developed for parallel G4 DNA targeting based on the concept of triggered disaggregation-induced emission (DIE). The designed probe is aggregated and nonfluorescent; in the presence of parallel G4 DNA, it disaggregates and produces a clear light-up fluorescence signal. AB-1 has been successfully applied for the optical discrimination of parallel vs. anti-parallel G4 and non-G4 DNAs. Mechanistic studies suggested that AB-1 stacks on the 5′-end G-quartet, which may explain the specificity of the probe to only a subset of parallel structures. In vitro studies with different cell lines showed that the probe was more cytotoxic to cancer cells. Moreover, the probe displayed good biocompatibility; it could enter live cells and localize in the cytoplasm, as shown by confocal fluorescence microscopy. This study provided structural details for the development of G4-specific probes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...