ZnSnO3–hBN nanocomposite-based piezocatalyst: ultrasound assisted reactive oxygen species generation for degradation of organic pollutants†
Abstract
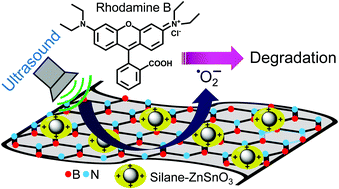
Piezocatalysis is an emerging water purification technology in which mechanical energy is used to degrade toxic chemicals by means of piezoelectric materials coupled with electrochemical surface reactions. However, the low efficiency of current piezocatalysts creates a serious bottleneck for their widespread applications. Herein, we report a zinc stannate and hexagonal boron nitride nanosheet (ZnSnO3–hBN)-based nanocomposite as an efficient piezocatalyst for degradation of organic pollutants under ultrasound irradiation. Compared to the piezocatalytic ZnSnO3 nanoparticle, its composite with hBN facilitates almost 4 times faster degradation of RhB. The room temperature ferroelectric property of the ZnSnO3–hBN nanocomposite is responsible for generating strong piezopotential and fast carrier transport. We found that superoxide radicals generated during piezocatalysis are the principal reactive oxygen species (ROS) responsible for the ultrasound assisted pollutant degradation phenomenon. The presented concept can be adapted for developing efficient piezocatalytic materials for ultrasound assisted water decontamination applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...