Synthesis of characteristic polyisoprenes using rationally designed iminopyridyl metal (Fe and Co) precatalysts: investigation of co-catalysts and steric influence on their catalytic activity†
Abstract
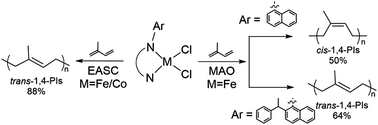
Based on iminopyridine ligands (L1–L3), Fe(II) (Fe1–Fe3) and Co(II) (Co1–Co3) complexes were synthesized and characterized well. According to single-crystal XRD studies, Co3 exhibits a dimeric structure with a four-coordinated metal center. Whereas, the iron complexes (Fe1 and Fe3) coordinate with two ligands to form a distorted-octahedral and distorted-trigonal bipyramidal geometry, respectively. All these catalysts were tested for the polymerization of isoprene. Using MAO as the co-catalyst, the Fe3 catalyst containing a bulky substituent can provide trans-1,4-unit (64%) polyisoprenes, while the Fe1 catalyst afforded trans-1,4-unit polyisoprenes (32%). Conversely, the combination of EASC as the co-catalyst with Fe1–Fe3 catalysts can give 1,4-unit polyisoprenes with high trans-1,4-unit selectivity (up to 88%). The central metal atom of the catalysts plays a crucial role in isoprene polymerization and significantly affects their activity. Fe(II) catalysts showed the highest activity (up to 99% yield), and afforded polyisoprenes with high molecular weights (191 kg mol−1). However, Co(II) systems exhibited lower activity (60% yield) and the obtained polyisoprenes were of lower molecular weights (2.15 kg mol−1) with broad molecular weight distribution.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...