Competition and cooperativity of hydrogen-bonding and tetrel-bonding interactions involving triethylene diamine (DABCO), H2O and CO2 in air†
Abstract
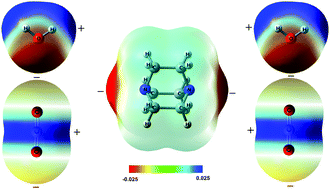
Triethylene diamine (DABCO) has the characteristic of being hydrophilic and exhibits a color change in air because its N atom can interact with H2O and CO2. To understand these phenomena, herein, theoretical calculations on the intermolecular interactions between DABCO and H2O (or CO2) were carried out at the M06-2X/aug-cc-pVDZ level without and with the counterpoise method, and single-point calculations at the CCSD(T)/aug-cc-pVDZ level were also performed. The electron donating ability of DABCO was revealed by the molecular surface electrostatic potential and Fukui function. The driving forces for the formation of a dimer and trimer were uncovered by EDA analyses. Because DABCO can interact with both H2O and CO2, the formation of hydrogen bonds and tetrel bonds is competitive, and meanwhile, DABCO can interact with H2O and CO2 simultaneously, so the hydrogen bond and tetrel bond can coexist and cooperate with each other. The hydrogen bond and tetrel bond in the dimers and trimers were proven and analyzed by NCI and QTAIM. The results presented here will provide useful insight in understanding the hydrophilic characteristic and the color change of DABCO.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...