Label-free fluorescence assay based on near-infrared B,N-doped carbon dots as a fluorescent probe for the detection of sialic acid†
Abstract
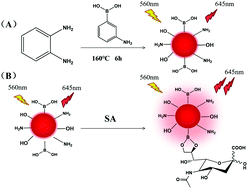
Near-infrared fluorescent nanomaterials are highly promising materials for biomedical applications because of their avoidance of the auto-fluorescence of organisms. We herein report a facile one-pot synthesis of near-infrared B,N co-doped carbon dots (CDs) by using o-phenylenediamine (OPD) and 3-aminophenylboronic acid (ABPA) as precursors. The prepared near-infrared B,N-doped carbon dots with a fluorescence emission wavelength of 645 nm have abundant boric acid groups on the surface of the CDs that can combine with the ortho-dihydroxy group of sialic acid (SA) to form a five-membered ring, leading to the formation of a CD/SA complex, which can enhance the fluorescence intensity of the CDs. Thus a simple and sensitive fluorescence method for the detection of sialic acid was established. The fluorescence intensity change of the system (F/F0) exhibited a good linear relationship with the concentration of sialic acid in the range of 20–1000 μM with a detection limit of 9.24 μM. This near-infrared fluorescent probe was successfully applied to the detection of sialic acid in simulating human saliva samples with satisfactory results.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...