All-electrochemical synthesis of a three-dimensional mesoporous polymeric g-C3N4/PANI/CdO nanocomposite and its application as a novel sensor for the simultaneous determination of epinephrine, paracetamol, mefenamic acid, and ciprofloxacin†
Abstract
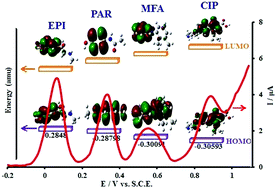
In this work, a three-dimensional mesoporous polymeric graphitic-C3N4/polyaniline/CdO (mpg-C3N4/PANI/CdO) nanocomposite was prepared as follows: C3N4 was synthesized via a green and one-step electrochemical method and then, step-by-step, C3N4, PANI, and CdO were electrochemically synthesized on the electrode surface. Field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM), energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX), Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction (XRD), Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) analysis and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) were used to characterize the nanocomposite. This nanocomposite was used for the first time as a high-performance electrochemical sensor for the determination of epinephrine (EPI), paracetamol (PAR), mefenamic acid (MFA) and ciprofloxacin (CIP). The simultaneous determination of these four species is challenging because they may coexist in the body and thus, measuring their concentrates with a sensitive and selective sensor is important. Cyclic voltammetry (CV) and differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) were applied for the determination. In addition, the highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) and lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO) eigenvalues of the EPI, PAR, MFA, and CIP molecules have been evaluated using the DFT method, and their HOMO energy has been used as the negative experimental ionization potential (-IP). The sensor provided two linear responses in the range of 0.05–80 μM and 100–1000 μM for EPI, one in the range of 0.1–790 μM for PAR, one in the range of 0.2–400 μM for MFA, and two in the range of 0.01–20 μM and 25–250 μM for CIP. The detection limits were 0.011 μM, 0.026 μM, 0.045 μM, and 0.005 μM (S/N = 3) for EPI, PAR, MFA, and CIP, respectively. The synthesized mpg-C3N4/PANI/CdO nanocomposite showed good reproducibility, stability and anti-interference electrocatalytic performance toward the simultaneous sensing of EPI, PAR, MFA, and CIP. In addition, the analytical application of the proposed sensor was successfully conducted for the determination of these species in real human serum samples.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...