A dihydronaphthalene based fluorescence probe for sensitive detection of cysteine and its application in bioimaging†
Abstract
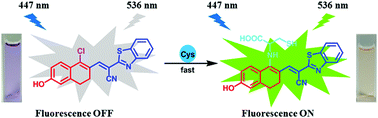
Cysteine (Cys) as an essential amino acid for life plays important roles in the synthesis of various proteins and human metabolism. The detection and monitoring of the concentration of cysteine in vitro and in vivo is significant for the diagnosis of related diseases. Herein, we designed and synthesized a novel fluorescent probe NC-Cys for the detection of cysteine, which employed dihydronaphthalene as the fluorophore. After the addition of Cys, colorimetric naked eye detection of Cys was achieved by the color change from purple to bright yellow. Moreover, the fluorescence intensity at 536 nm in the presence of Cys showed about a 90-fold fluorescent signal increase compared to that with no Cys addition. The probe NC-Cys exhibited satisfactory sensitivity and selectivity to Cys. A good linear relationship between I536 and the concentration of Cys (0–100 μM) was also observed with a calculated detection limit of 2.1 × 10−8 M. Importantly, the probe NC-Cys was successfully applied in the fluorescence imaging of Cys in living cells and tissues with low cytotoxicity. This newly developed fluorescent probe would be a potentially useful tool for the imaging of Cys in wider physiological and pathological processes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...