Structural, luminescence and geno/cytoxicity study of carbon dots derived from Opuntia ficus-indica (L.) Mill
Abstract
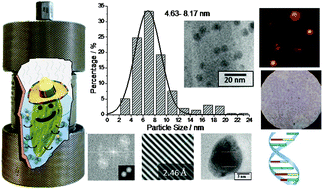
Photoluminescent carbon dots (CDs) were synthesized by the hydrothermal method. In the synthesis, different plants as carbon sources were used. Photoluminescence results demonstrated the highest emission for CDs coming from nopal. Therefore, different concentrations of nopal during the CD syntheses were evaluated to determine the maximum emission intensity. Transmission electron microscopy revealed a narrow particle distribution (5–7 nm). Furthermore, the indexed planes (213) and (203) demonstrated the hexagonal phase of these CDs. Chromatic coordinates x = 0.157 and y = 0.158 confirmed blue emission according to the CIE diagram. The genotoxic and cytotoxic potential of nopal CDs were evaluated with the micronucleus test in mice, and with the relationship between young and mature erythrocytes, also in mice. Five doses of CDs were tested by the intravenous route (0.02, 0.2, 2, 25, and 50 mg kg−1). Results obtained in micronuclei showed that all tested doses were genotoxic, except the two low doses at 96 h of the assay. With respect to cytotoxicity, the CDs also induced a bone marrow proliferation decrease along the assay, particularly 48 h after exposure. Thus, our geno/cytotoxicity assay revealed that the CDs were able to damage DNA and to cause cytotoxicity, and also suggested that biomedical approaches can be preferable assayed at the lowest tested dose range (0.02 mg kg−1).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...