Red mud modified with graphene oxide for enhanced visible-light-driven photocatalytic performance towards the degradation of antibiotics†
Abstract
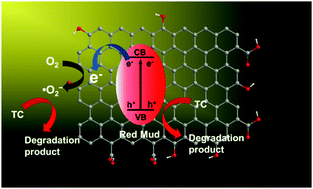
Widely used antibiotics have been caused serious environmental pollution. Thus, it is imperative to prepare photocatalysts with high activity and stability to remove them. In this work, a red mud/graphene oxide (RM–GO) composite was prepared using a facile synthetic method. The photocatalytic efficiency of RM and RM–GO composites was investigated by degrading tetracycline (TC, 10 mg L−1) in visible light (λ > 420 nm). The results show that the RM–GO composite exhibits improved photocatalytic activity compared to RM-raw and RM-7GO (the mass ratio of RM to GO is 93 : 7) shows the best photocatalytic performance (the degradation rate of TC is 79.8% within 80 min). Additionally, the degradation effect on other antibiotics, including oxytetracycline and chlortetracycline, was investigated to confirm its good applicability. The improvement in photocatalytic activity can be attributed to improved light absorption, specific surface area, and charge separation of GO for RM. This work provides an effective way to improve the photocatalytic activity of RM for treating waste-water containing wastes, which is beneficial for resource utilization and environmental protection.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...