A compact prospective investigation on the colorimetric recognition of Hg2+ ion and photostimulated degradation of discharged toxic organic dyes motivated by H. mutabilis directed silver nanoparticles†
Abstract
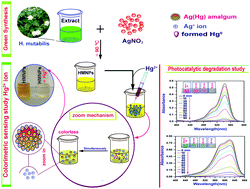
Current researches on detrimental chemical hazards have successfully put forward the noxious effects of toxic metal ion and released harmful organic dyes (such as TB and Rh-B) upon discharge into the environment. However, the exposure of Hg2+ ions is the most alarming among all. In order to get rid of its deleterious effects, the detection of Hg2+ ion is urgent. Motivated by this, we have for the first time presented an accurate picomolar level detecting colorimetric sensor stabilized by Hibiscus mutabilis leaf extract. It manifested outstanding selectivity, superb single shot response, and high sensitivity towards Hg2+ ion with a reliable detection limit of 48 pM. Moreover, our synthesized nanoparticles were found eligible as a capable photon induced catalyst for the degradation of commercially discharged toxic anthropogenic organic dyes TB and Rh-B, which were degraded up to 94% and 97%, respectively. The used experimental approaches to support our investigation were UV-Vis, DLS, HRTEM, XRD, FESEM, XPS, and zeta potential analysis. It was ensured that Ag(Hg) amalgam formation was the mechanism for the detection of Hg2+ ion. Intriguingly, the sensitivity of the system was progressively promoted to a lower detection limit (30 pM) in the presence of high salt concentration. We anticipate that this research could pose revolutionary impact and can encourage the scientists to follow the “go green” strategy for the development of risk free supplementary nanoparticles to fight against environmental hazards.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...