Relevant electronic interactions related to the coordination chemistry of tetracyanometallates. An XPS study†
Abstract
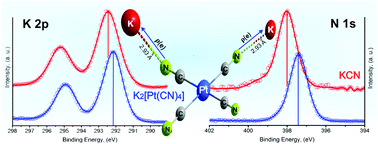
The π-back donation in cyanometallates is responsible for pronounced electron density redistribution in the complexes and their salts. The most relevant physical and functional properties of transition metal cyanides are related to that charge redistribution. This contribution discusses such an effect from XPS data for a series of tetracyanometallates. The following compositions: K2[M(CN)4]·xH2O (M = Ni, Pd, Pt), T[Ni(CN)4]·xH2O (T = Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn), Ni[Pd(CN)4]·xH2O and Ni[Pt(CN)4]·xH2O were considered for this study. The π-back donation is appreciated as an accumulation of the electron density on the N end of the CN ligand. In the potassium salts, that increase of negative charge on the N atom is responsible for a strong interaction with the potassium ion, involving certain charge transfer to this last one. On coordination polymer formation, T[M(CN)4]·xH2O, part of that electron density, accumulated on the N end, is donated to the metal (T), resulting in a new charge redistribution process that is sensed by the binding energy of the involved atoms. For such charge variation, related to the π-back donation and then during the coordination polymer formation, XPS appears as an excellent sensor. This is the first systematic study on XPS application to the coordination chemistry of tetracyanometallates. The information obtained from XPS spectra was complemented with structural (XRD) and TG data, and IR, Raman and UV-vis spectra.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...