Development of an optically transparent polysilsesquioxane/PDMS addition cured nanocomposite adhesive for electronic applications
Abstract
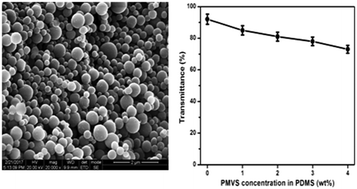
There is an increasing demand for polymer nanocomposites that have optical transparency alongside high mechanical and thermal properties for specific applications. We report herein a series of optically clear addition cured polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) nanocomposites that were prepared using a hydrosilylation method with poly(methy/vinyl)silsesquioxane (PMVS) nanospheres as a reinforcing agent and platinum as a catalyst. The PMVS nanospheres were synthesized via the hydrolytic condensation of organosilane as a precursor in the aqueous phase. The influence of the PMVS nanospheres on the morphology, mechanical properties, thermal stability, thermal conductivity, adhesive strength and optical transparency of these addition cured PDMS nanocomposites was studied in detail. It was observed that the tensile strength and thermal stability of the nanocomposites were enhanced upon the addition of PMVS nanospheres. These prominent improvements in the mechanical properties were attributed to the strong interactions between the PDMS chains and uniformly dispersed PMVS nanospheres in the polymer matrix. The optical transparency of the nanocomposites was not greatly affected by the incorporation of PMVS owing to the compatibility and low mixing viscosity of the nanocomposites. The lap shear strength of the PDMS nanocomposites on mild steel substrate shows significant enhancement when compared to the neat composite adhesive.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...