The inhibition effect and deactivation mechanism of H2O and SO2 on selective catalytic oxidation of NO over the Mn–Ca–Ox–(CO3)y catalyst
Abstract
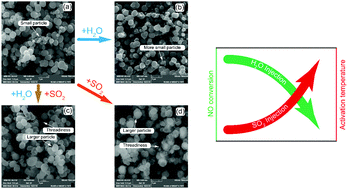
The Mn–Ca–Ox–(CO3)y catalyst was used in this work for selective catalytic oxidation of NO. The influences of SO2, H2O and H2O + SO2 on the deactivation process were investigated. Surface morphology and pore structure analyses indicated that SO2 reacted with the catalyst to form larger particles and H2O could react with MnCO3 to form smaller particles. The XRD results showed that the deactivation product under SO2 atmospheric conditions was MnSO4. The XPS results showed that H2O could promote the formation of MnO2. The H2-TPR results indicated that the influence of H2O on oxidation activity sites was weak. Meanwhile, the introduction of SO2 increased the activation temperature. The DRTFIR experimental results indicated that SO2 had a direct chemical interaction with the catalyst and the formation of MnSO4 does not rely on O2. O2 enhanced the chemical interaction between SO2 and the catalyst. SO2 adsorbed on the catalyst surface prior to NO. The SO2 deactivation process was irreversible and it was attributed to chemical deactivation. H2O inhibited the transformation from nitro to NO2 and the H2O deactivation process was attributed to physical deactivation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...