In vitro and in vivo anticancer activity of a thiourea tripyridyl dinuclear Cu(ii) complex†
Abstract
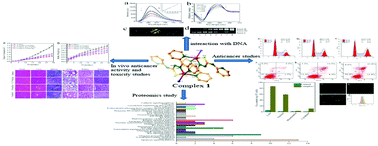
Metal-based anticancer drugs have been gaining attention recently. In this study we identified and characterized a dinuclear complex, [Cu2(dppc)2I2] (1) (dppc = 2-(di(pyridin-2-yl)methylene)-N-(pyridin-2-yl)hydrazine-1-carbothioamide). Complex 1 showed a high cytotoxicity against tumor cells, including SMMC7721 (live tumor cell line), HCT116 (colon tumor cell line), and TFK-1 (cholangiocarcinoma cell line), but not for L-02 (normal human liver cell line), and SMMC7721 cells showed the most sensitivity. Analyzing the uptake and distribution of complex 1 in the SMMC7721 cells revealed that the complex was mainly localized in the nucleus. Complex 1 could bind to ctDNA via insertion and effectively cleave the pBR322 DNA. Through the results of flow cytometry analysis, we observed a significant increase in the levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and Ca2+ in the SMMC7721 cells. Additionally, we observed that there was a loss of mitochondrial membrane potential and that the cell cycle was arrested in the G2/M phase. Differential protein expression analysis indicated that complex 1 could activate multiple apoptotic signaling pathways, including the p53 pathway. In vivo studies using a xenograft bearing nude mouse model further demonstrated that complex 1 also exhibited a remarkable inhibitory effect on the tumor growth with no marked side effects.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...