In situ analysis of pesticide residues on the surface of agricultural products via surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy using a flexible Au@Ag–PDMS substrate†
Abstract
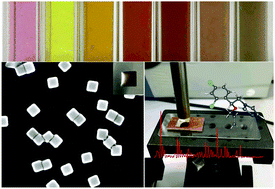
Pesticide residues have been the focus of widespread attention in the field of food safety. Here, we describe a new portable polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) flexible surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) substrate decorated with silver-coated gold nanocubes (Au@Ag NCs) to rapidly measure pesticide residues on the surface of agricultural products. The finite difference time domain (FDTD) method and density functional theory (DFT) were used to optimize the preparation of the substrates, and the attribution of the imazalil (IMZ) characteristic peaks is discussed in detail. The relationship between the concentration obtained by in situ SERS detection and the maximum residue limits (MRLs) of pesticides was established accurately by three mass measurements. The minimum pesticide concentration on the surface could reach 2 mg L−1, which corresponds to an apple's MRL of just 0.073 mg kg−1. The feasibility of this method was further verified by the detection of phosmet pesticide residues. The results demonstrated that the method has great potential for detection of low-concentration pesticides.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...