Corncob-derived hierarchical porous carbons constructed by re-activation for high-rate lithium-ion capacitors†
Abstract
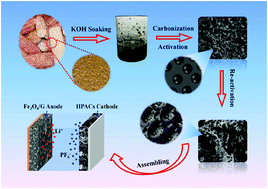
A lithium-ion capacitor (LIC) is a promising energy storage device, combining both high energy density and high power density. Biomass derived carbon is an appealing positive electrode material for LICs due to its plentiful porous structure, large surface area, and high electrical conductivity. However, its electrochemical performance has been limited because of the low graphitization and uncontrollable porous structure obtained from the conventional approach. Herein, novel hierarchical porous activated carbons (HPACs) from corncob were prepared by a re-activation method. All HPAC samples have unique bimodal pore structures, containing micropores for charge storage and mesopores for electrolyte ion migration. The optimal HPACs-1-2 possesses large surface area (2351 m2 g−1), optimized bimodal pore size distribution, and high graphitization. Therefore, HPACs-1-2 displays a high specific capacitance of 187 F g−1 at 1 A g−1 and exciting rate performance. In addition, the LIC based HPACs-1-2 cathode and Fe3O4/G anode deliver a superior energy density of 102 W h kg−1 at a power density of 536 W kg−1 and show excellent cycling life with 82% of the initial specific capacitance after 2000 cycles.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...