Novel 5-chloro-pyrazole derivatives containing a phenylhydrazone moiety as potent antifungal agents: synthesis, crystal structure, biological evaluation and a 3D-QSAR study†
Abstract
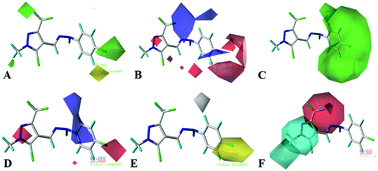
Based on the active substructure combination principle, twenty-four novel 5-chloro-pyrazole derivatives containing a phenylhydrazone moiety were designed, synthesized, and evaluated for their antifungal activity. Their structures were confirmed using 1H NMR, 13C NMR, and HR-MS spectra. The single-crystal structure of compound 8a was analyzed emphatically using X-ray diffraction. The antifungal activities against Fusarium graminearum, Botrytis cinerea, and Rhizoctonia solani were evaluated in vitro. The results of the bioassays revealed that most of the target compounds showed obvious fungicidal activity. Strikingly, the compound 7c exhibited the most potent activity with EC50 values of 0.74, 0.68, and 0.85 μg mL−1 against the above three plant pathogenic fungi, respectively. The compounds 7c, 8d, and 8g showed significant bioactivity against R. solani with EC50 values of 0.85, 0.25, and 0.96 μg mL−1, respectively. In addition, CoMFA and CoMSIA molecular modeling was performed for a 3D-QSAR study, and presented a good predictive ability with q2 values of 0.575 and 0.667, and r2 values of 0.961 and 0.962, respectively. The results provide useful information for guiding the design and synthesis of novel potent pyrazole derivatives with good antifungal activity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...