A selective and sensitive peptide-based fluorescent chemical DSH sensor for detection of zinc ions and application in vitro and in vivo†
Abstract
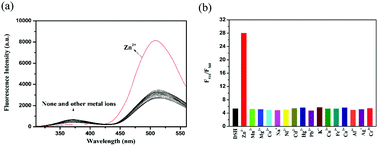
In recent years, the design and application of peptide-based fluorescent chemical sensors has been the subject of extensive research due to several technological advantages, including the technological maturity of solid phase peptide synthesis and side chain modifications, and the fact that peptide-based fluorescent chemical sensors exhibit good water solubility, biocompatibility and low toxicity, making them widely-applicable in environmental monitoring, bioimaging, medical diagnosis and disease treatment. The recognition mode of peptide-based fluorescent chemical sensors can be easily realized by different recognition mechanisms, such as photoinduced electron transfer (PET), fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) and chelation enhanced fluorescence (CHEF). Here we report the design and synthesis of a peptide-based fluorescent chemical sensor (DSH sensor: Dansyl-Ser-Pro-Gly-His-Trp-Gly) for detecting Zn2+, based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) from tryptophan (donor) to the dansyl fluorophore (acceptor). Results of this study indicate that the DSH sensor has potent selectivity and sensitivity to Zn2+, with an approximate limit of detection (LOD) of 124 nM in vitro. In addition, the DSH sensor can penetrate cells, exhibit low toxicity and stable fluorescence emission intensity, and may detect the concentration of Zn2+ in a complex biological environment for live cell imaging.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...