Epoxy/methyl methacrylate acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (MABS) copolymer blends: reaction-induced viscoelastic phase separation, morphology development and mechanical properties
Abstract
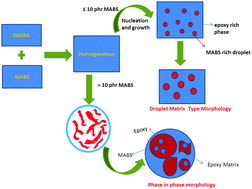
This article examines for the first time the effect of the addition of methyl methacrylate acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (MABS) copolymer on the phase separation, morphology and mechanical properties of epoxy systems. Blends of epoxy resin/MABS containing 5, 10, 15 and 20 phr MABS were prepared using a solution mixing technique. The homogenous blends obtained by this technique undergo a polymerization reaction-induced phase separation process by the introduction of the curing agent 4,4′-diaminodiphenyl sulfone (DDS). The optical microscopy analyses revealed that at low concentration of the MABS, the phase separation was by a nucleation and growth process. However, at higher concentration of MABS, the phase separation was by a spinodal process as evidenced by the formation of a co-continuous phase morphology followed by coarsening at later stages leading to phase separated domains. The morphology of the completely cross linked samples was probed by SEM, TEM and AFM analyses. A phase-in-phase morphology was noticed in all the compositions as a result of a viscoelastic phase separation process due to strong dynamic asymmetry arising from the molecular weight and Tg differences between the component polymers (high molecular weight MABS and liquid epoxy). In other words, the phase separated MABS and epoxy phases were not pure phases, both had sub-inclusions of the other phase leading to an interpenetrating polymer network (IPN) type of structure. The dynamic mechanical spectroscopy data also indicated a phase-in-phase morphology as evidenced by the shift in the Tg of the phases. It was also observed that the mechanical properties of the blends were enhanced effectively by the addition of MABS. The tensile strength and impact strength of epoxy increased by 25% and 72%, respectively, upon loading of MABS. This article also provides a correlation between the morphology and mechanical properties of the blended systems.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...