Revisiting the fluoride binding behaviour of dipyrrolylquinoxaline in aqueous medium: a copper ion mediated approach†
Abstract
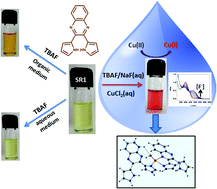
An ion detection methodology employing synergistic interaction between copper(II) ions and fluoride with 2,3-dipyrrol-2′-yl-quinoxaline (SR1) is investigated with a particular target to detect fluoride in an aqueous environment. The theme of this work simultaneously exploits the H-bonding and metal–ligand interactions of SR1 in the presence of fluoride and Cu(II) ions in a DMSO/water mixture. The cooperative ion detection event in the presence of SR1 and fluoride reveals in situ reduction of Cu(II) to Cu(I) species, which causes a sharp colorimetric change from green to red differentiable to the naked eye. The mechanism of the reaction is comprehensively investigated using UV-Vis, 1H NMR, 19F NMR, EPR spectroscopy and Differential Pulse Voltammetry (DPV) techniques, and is further justified by DFT study and subsequent NBO analysis. The limit of detection (LOD) is found to be 0.15 ppm, which is below the limit set by WHO for the fluoride content in drinking water. The real time application of the protocol is also tested in groundwater samples collected from a fluoride affected area and toothpaste samples.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...