Computational investigation of the α2β1 integrin–collagen triple helix complex interaction†
Abstract
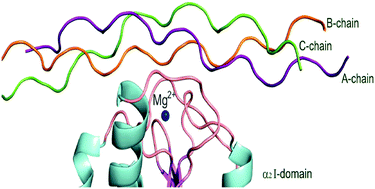
The greatest difficulty for the development of drugs targeting the α2β1 integrin, a transmembrane receptor that facilitates cell-extracellular matrix (ECM) adhesion, is the current understanding of its interaction with ligands, such as the collagen molecule – one of the most complex cell adhesion systems. In this sense, this work performs a quantum biochemistry analysis of the interaction between the α2β1 I-domain integrin and a collagen structure containing the GFOGER (Glycine–Phenylalanine–Hydroxyproline–Glycine–Glutamate–Arginine) sequence. Our study was carried out by using the Molecular Fractional with Conjugate Caps (MFCC) method within Density Functional Theory (DFT) with generalized gradient approximations (GGA), and Grimme's long-range dispersion correction. Our results confirm the importance of the amino-acids residues Thr221, Asp219, Asp254 and Glu256 (Arg12, Glu33, Arg34, Glu55 and Arg56) present in the MIDAS – Metal Ion Dependent Adhesion Site – region (GFOGER motif) of the integrin–collagen interaction. Besides, we depicted the relevance of each strand (A, B and C chains) in the triple-helical collagen structure, helping the understanding of the events involving the interaction integrin–collagen.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...