A polyaniline@MoS2-based organic–inorganic nanohybrid for the removal of Congo red: adsorption kinetic, thermodynamic and isotherm studies†
Abstract
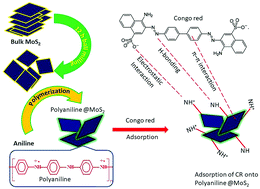
Organic–inorganic functional hybrid polymeric materials are well known for the efficient removal of contaminants from wastewater. Herein, mechanical exfoliation of bulk MoS2 and its composite with polyaniline (Pani@MoS2) via facile in situ oxidative polymerization has been reported. The application of the Pani@MoS2 hybrid adsorbent to the scavenging of the organic pollutant dye Congo red (CR) from an aquatic environment in batch experiments has been investigated. The adsorption and removal of CR using Pani/MoS2 was much higher than the bulk and exfoliated MoS2 nanosheets. The effects of varying experimental conditions, such as pH, temperature, CR concentration, and interaction time between the adsorbent and CR at which optimal removal occurs, were examined. The highest adsorption of 70.921 mg g−1 was recorded at 120 min, pH 5, and 50 °C and was due to the π–π and electrostatic interactions between the nitrogen containing groups of the adsorbent and CR molecules. The adsorption equilibrium data were well fitted to the Langmuir adsorption isotherm model, revealing monolayer coverage of the CR molecules on the Pani@MoS2 nanohybrid adsorbent. The CR adsorption kinetics and thermodynamics were also studied to gain a better understanding of the adsorption mechanism and the interaction between the CR molecules and the active sites present on the Pani@MoS2 nanohybrid. The results show that Pani/MoS2 is an efficient adsorbent for the removal of CR dye from wastewater.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...