Synthesis, crystal growth, physio-chemical characterization and quantum chemical calculations of NLO active metal–organic crystal: dibromo(4-hydroxy-l-proline)cadmium(ii) for non-linear optical applications†
Abstract
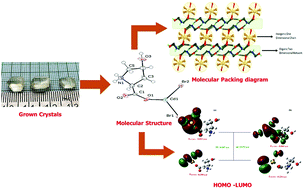
Single crystals of a new metal–organic compound, dibromo(4-hydroxy-L-proline)cadmium(II), (DB4HPC), of 10 × 5 × 3 mm in size were crystalized in a non-centrosymmetric space group via a slow evaporation solution method. Solubility studies were then carried out using deionized water. The crystal structure of the compound was ascertained from single-crystal X-ray diffraction measurements. The results reveal that the grown crystal belongs to a monoclinic crystal system with the space group P21. EDS measurements were carried out to confirm the elements present in the compound. The molecular structure of the compound and its vibrational behavior were analyzed by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and Fourier-transform infrared (FT-IR) spectral studies, respectively. A UV-vis-NIR study showed that DB4HPC has a wide transmission window [60%] over the entire visible region. The optical band gap of the crystal was estimated from the Tauc plot as 4.82 eV. The thermal stability of the compound was measured by thermogravimetry analysis (TGA) and differential thermal analysis (DTA), respectively. Growth pattern and surface features were analyzed in chemical etching studies. The mechanical stability of the compound was determined from Vickers microhardness measurements. The nonlinear optical properties of the material were confirmed using the Kurtz and Perry technique and the second harmonic generation efficiency of DB4HPC was found to be 2.5 times that of pure KDP. The first-order molecular hyperpolarizability (β0), dipole moment (μ), and polarizability (α) of the present molecule were evaluated using Density Functional Theory (DFT) employing a B3LYP functional, and the LanL2DZ basis set with the help of the Gaussian 09W program. The optimized geometry was found to closely resemble the experimental crystal structure. The frontier orbital HOMO–LUMO gap was also determined to understand the chemical reactivity and kinetic stability of the title compound. The values of various global chemical molecular reactivity descriptors such as chemical hardness (h) were calculated. All of the results show that the metal–organic compound DB4HPC is promising for use in non-linear optical (NLO) applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...