Enhanced bactericidal and photocatalytic activities of ZnO nanostructures by changing the cooling route†
Abstract
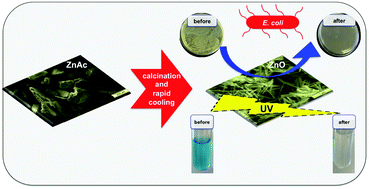
We report on a simple synthesis of ZnO nanowires by calcination of zinc acetate. The effect of calcination temperature and cooling route on the antibacterial and photocatalytic properties is demonstrated by varying the size and surface area of the nanowires. The decrease of the calcination temperature followed by a rapid cooling procedure leads to a smaller size and larger surface area of the nanowires. ZnO nanowires are found to be effective against the growth of E. coli at the microgram level. In addition, the photocatalytic activity of the synthesized ZnO nanowires is demonstrated by the successful degradation of the organic dye methylene blue.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...