High current density cation-exchanged SnO2–CdSe/ZnSe and SnO2–CdSe/SnSe quantum-dot photoelectrochemical cells†
Abstract
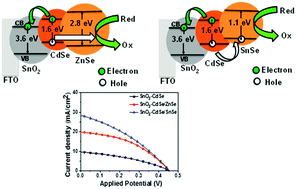
Research on the combination of low and high-bandgap energy materials through an ion-mediated chemical transformation of the nanostructure of one material into another, especially metal chalcogenide quantum dot (QD) solar cells plays a very important role in the fast charge transformation process with high power conversion efficiencies (PCE) by reducing surface charge recombinations. Based on a coordination chemistry approach, the present study demonstrates the importance of cation-exchange process in developing bandgap engineering of tin oxide–cadmium selenide (SnO2–CdSe) with zinc selenide (ZnSe) and tin selenide (SnSe) to form SnO2–CdSe/ZnSe and SnO2–CdSe/SnSe electrodes, respectively. Experimental conditions are optimized from optical and photovoltaic performances. Our best performing cation-exchange interface-modified photoelectrochemical devices, i.e., SnO2–CdSe/ZnSe and SnO2–CdSe/SnSe have achieved improvements of 21% and 28%, respectively, in their PEC values, i.e., 3.78% and 4.41% with remarkable current densities of 19.82 and 28.40 mA cm−2 when compared with SnO2–CdSe (1.63% and 9.74 mA cm−2). This is due to (a) the fast transfer of photo-generated electrons from the CdSe QD sensitizer to SnO2 photoanode by engineering a synergistically favourable band gap and (b) mitigation of a reverse photogenerated electron flow in the presence of a high band gap buffer ZnSe/SnSe layer, which would otherwise cause excessive recombinations. A simple cation-exchange interface modification process can, in general, pave the way for improving the performance of QD-based solar cells.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...