Facile synthesis of core–shell Ag@C nanospheres with improved tribological properties for water-based additives
Abstract
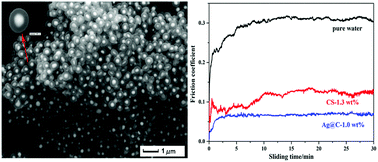
In this study, silver nanoparticles (NPs) were successfully encapsulated in a carbonaceous shell to form core–shell Ag@C nanospheres using a one-step green hydrothermal method, which involved reduction of AgNO3 and catalyzing the carbonation of aqueous glucose solution. Simultaneously, the Ag core with a diameter of about 130–180 nm and carbon shells with size ranging from 100 to 120 nm were characterized by field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The surface of Ag@C nanospheres had abundant oxygen-containing functional groups, which were beneficial to their dispersion in water. The tribological behavior of Ag@C nanospheres as a water-based additive was investigated using a MS-T3000 ball-on-disk tribometer. The water sample with 1.0 wt% Ag@C nanospheres exhibited 80.6% and 40.4% reduction in the friction coefficient and wear scar width, respectively, compared to pure water. The improved tribological performance of Ag@C nanospheres was ascribed to their perfectly spherical structure, which acted as a rolling bearing between the friction counterparts. Moreover, the Ag core provided internal support through a three-dimensional contact between the Ag nucleus and carbon shell. Therefore, the Ag@C nanospheres showed significant prospects for water-based lubricants.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...