Interactions between the antiviral drug telaprevir and human serum albumin: a combined study with spectroscopic methods and molecular modeling†
Abstract
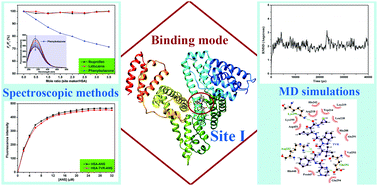
Telaprevir (TVR) is a first-generation protein inhibitor approved in 2011 for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C, a global epidemic that threatens the human health. This study investigated the interaction between TVR and human serum albumin (HSA) by combining spectroscopic methods and molecular modeling. Fluorescence experiments indicated that TVR could bind to HSA through a static process with a moderate affinity, and the static mechanism was confirmed by time-resolved fluorescence spectroscopy. Negative free energy change obtained from thermodynamic parameters suggested a spontaneous binding reaction between TVR and HSA. Hydrogen bonds and van der Waals force were found to play major roles in the binding process, according to the negative enthalpy and entropy changes. Molecular dynamics (MD) simulation further verified the driving forces, and indicated that hydrophobic force and electrostatic interactions were also involved in the binding. The site I binding mode was demonstrated by site marker displacement experiments and MD simulations. The TVR–HSA complex was stabilized after 30 ns with a binding energy of about −298.4 KJ mol−1, and a less compacted HSA was induced by binding with TVR. Moreover, binding with TVR caused microenvironmental and conformational changes in HSA, based on their synchronous fluorescence, three-dimensional fluorescence, and circular dichroism spectra.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...