Porous CuO nanofibers derived from a Cu-based coordination polymer as a photocatalyst for the degradation of rhodamine B†
Abstract
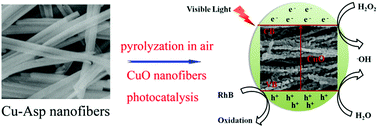
Coordination polymer- or metal–organic framework (CP/MOF)-derived metal oxides with diverse morphologies and microporous structures have shown potential applications in heterogeneous catalysis. In this study, porous CuO nanofibers were successfully synthesized by thermal treatment of a copper-based coordination polymer nanofiber (Cu(L-aspartic acid)·x(H2O), Cu-Asp) at different temperatures in a muffle furnace. The as-obtained CuO-T (T = 400, 500, and 600 °C) nanofibers comprised many inhomogeneous nanoparticles and inherited the fiber shape from the Cu-Asp precursor. The photocatalytic properties of the CuO-T nanofibers were tested towards a rhodamine B (RhB) solution in the presence of H2O2 under visible light irradiation. Experimental results reveal that the porous CuO-500 nanofibers show remarkably high photocatalytic activity, and the degradation rate reaches 96% within 160 min. The excellent photocatalytic performance of porous CuO-500 nanofibers can be ascribed to the porous structure, which causes low mass transport limitation and allows the dye molecules to easily access the photocatalytic active sites. Moreover, the CuO-500 nanofibers exhibit remarkably high photochemical stability. Furthermore, the possible photodegradation mechanism for the RhB dye using CuO-500 nanofibers is proposed based on the analysis of the involved active species. The results show that holes (h+) play a predominant role in the RhB oxidation process.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...