Organic nanoparticles of acetohydrazides as novel inhibitors for mild steel corrosion
Abstract
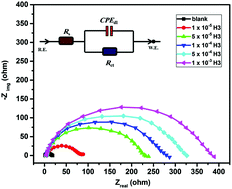
Novel organic nanoparticles (ONPs) of (E)-2-(4-(hydrazonomethyl)phenoxyl) acetohydrazide (H2) and N′((E)-benzylidene)-2-(4-((E)hydrazonomethyl)phenoxyl)acetohydrazide (H3) were prepared by the re-precipitation method. The ONPs were characterized using MS, 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR, FT-IR, DLS, TEM and XRD. Both nanoparticles revealed a hemispherical shape with a particle size of 3.0 nm and 2.0 nm for H2 and H3 nanoparticles, respectively. The protective effect of the ONPs on mild steel in 1.0 M HCl was monitored by polarization, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and atomic force microscopy (AFM). The obtained results revealed that the inhibition efficiency increased with an increase in inhibitor concentration. The maximum inhibition efficiencies at a constant concentration of 1 × 10−3 M were 88.2% and 96.7% for H2 and H3, respectively. The inhibition mechanism depended on the physical adsorption of the nanoparticles on the steel surface, which was confirmed by SEM, AFM and impedance results. These novel nanomaterials showed great anti-corrosion behavior and thus can be potentially used in industrial applications such as cooling water systems, pipes, and oil production units.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...