Cooperative role of halogen and hydrogen bonding in the stabilization of water adducts with apolar molecules†
Abstract
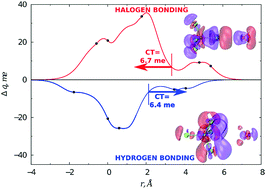
The relative role of halogen and hydrogen bonding in the stabilization of water adducts with apolar molecules is investigated by an integrated experimental–theoretical study. Molecular beam scattering experiments led to the characterization of the gas phase behaviour of H2O–CCl4 and H2O–CF4 systems, with the determination of the absolute scale of the interaction. Highly accurate ab initio calculations allow identifying the most stable energy configurations and the electron charge transferred upon adduct formation. The combined study is important to unambiguously identify the role of various components in the interaction (electrostatic, dispersion, induction and charge transfer) and for formulating a reliable model of the interaction potential. Our results suggest that, while the water–CF4 adduct is basically bound through the balance between size (Pauli) repulsion and dispersion attraction, an appreciable intermolecular bond stabilization by charge transfer is operative in water–CCl4. We identified a sizable charge transfer not only from H2O to CCl4, mostly for the vertex (halogen bonding) configuration, but also from CCl4 to H2O, for configurations where an H atom points at a chlorine centre, thus evidencing a hydrogen bond.
- This article is part of the themed collection: The halogen bond: a new avenue in recognition and self-assembly


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...