A highly sensitive glucose sensor based on a gold nanoparticles/polyaniline/multi-walled carbon nanotubes composite modified glassy carbon electrode
Abstract
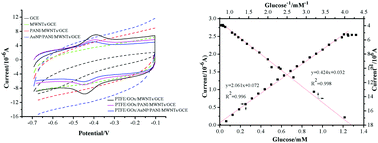
An amperometric glucose sensor, PTFE/GOx/AuNPs/PANI/MWCNTs/GCE, was assembled layer-by-layer using multi-wall carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs), polyaniline (PANI), and gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) for electrode surface modification and a fixed glucose oxidase enzyme (GOx) carrier. Methods such as cyclic voltammetry (CV) and chronoamperometry (CA) were used to investigate the performance of the modified materials and the sensor itself. The sensor responded well to glucose, and the enzyme fixed on the sensor experienced direct electron transfer (DET). The redox peak current for GOx exhibited a good linear relationship to the scan rate. The apparent heterogeneous electron transfer rate constant, K, was 5.19 s−1 (n = 2); the sensor reached 95.0% of the maximum stable current in 10 s. Moreover, the linear range for the glucose concentration was 0.0625 mM to 1.19 mM with a sensitivity of 29.17 μA mM−1 cm−2 and a detection limit of 0.19 μM. The sensor retained 92.0% of its initial activity after 30 days. The average relative standard deviation for the serum sample measurements was 2.3% (n = 3). The recovery rates ranged from 97.3% to 104.1% for various glucose concentrations. The results indicate that the PTFE/GOx/AuNPs/PANI/MWCNTs/GCE sensor can measure the glucose concentration in human serum and holds potential for future clinical applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...