Exploring the potential of newly synthesized 4-methyl-6-morpholino-pyrimidine derivatives as antiproliferative agents†
Abstract
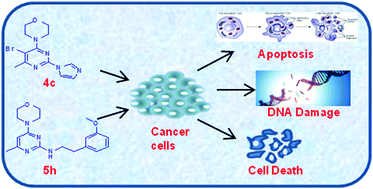
In view of exploring the potential of pyrimidine derivatives as anticancer agents, a series of 4-methyl-6-morpholinopyrimidine derivatives was synthesised and characterised by NMR (1H & 13C), SC-XRD and mass spectral analysis. The in vitro anticancer activity of these compounds was investigated using different human cancer cell lines, namely HeLa (cervix), NCI-H460 (lung), MCF-7 (breast), HepG2 (liver) and IMR-32 (brain). Compounds 4c and 5h exhibited potent anticancer activity in a dose-dependent manner as compared to other derivatives, with IC50 values of 5.88 ± 1.22 and 6.11 ± 2.12 μM on HeLa and NCI-H460, cells respectively. The inhibitory effect of 4c and 5h on cancer cell proliferation was shown to be a consequence of reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation and subsequent induction of cellular apoptosis, as evidenced by an increase in hypodiploid (subG1) population, early apoptotic cell population, caspase-3/7 activity, loss of mitochondrial membrane potential and degradation of nuclear DNA. Furthermore, molecular docking studies revealed that 4c and 5h compounds bind to the ATP binding pocket of the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR). Based on our results, we conclude that 4-methyl-6-morpholinopyrimidine derivatives prevent cancer cell proliferation by inducing apoptosis and thus have potential to be further explored for anticancer properties.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...