Novel synthesis of Ag decorated TiO2 anchored on zeolites derived from coal fly ash for the photodegradation of bisphenol-A†
Abstract
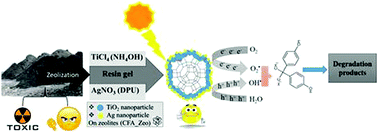
The disposal of millions of tons of coal fly ash (CFA) threatens the environment, hence means to reuse CFA are highly sought after. In this study, CFA was reused to make materials which were tested for water purification. Zeolitic material (CFA_Zeo) was derived from CFA by a 2-step alkali-fusion hydrothermal method and then composited with TiO2 nanoparticles using a novel resin-gel technique. CFA_Zeo loadings were 15 and 30 wt% in the resulting TiO2/CFA_Zeo composites. These composites were then loaded with 1 wt% Ag nanoparticles by a deposition–precipitation technique using NaOH and urea. CFA_Zeo rods (morphology confirmed by TEM) were confirmed by PXRD to be sodium aluminum silicate hydrate. TEM analyses of the CFA_Zeo rods in the composites revealed them to be completely coated with TiO2 nanoparticles that had Ag nanoparticles on their surfaces. The photoluminescence emission peak of TiO2 was found to be significantly higher than that of TiO2/CFA_Zeo composites, with the TiO2/CFA_Zeo composites that were loaded with Ag having even lower emission intensities. UV-vis DRS spectra showed that CFA_Zeo had no effect on the band gap of TiO2, while composites that contained Ag had a wide absorption band in the visible region. The photocatalytic efficiency of these materials was then determined using bisphenol-A (BPA) as a model compound under both UV and visible light. Except for the 30 wt% TiO2/CFA_Zeo composites without Ag, all of the composites had superior photoactivity to uncomposited TiO2 under both UV and visible light. On the other hand, composites with Ag nanoparticles showed the best photoactivities. The superior photoactivities of these composites under UV-light were mainly attributed to the separation of charge carriers, whereas under visible light it was attributed to the ability of silver to harvest visible light through surface plasmon resonance (SPR).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...