Heterogeneous lyophobic systems based on pure silica ITH-type zeolites: high pressure intrusion of water and electrolyte solutions†
Abstract
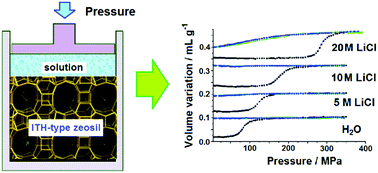
The energetic performances of pure silica ITH-type zeolites were studied by high pressure intrusion–extrusion in water and LiCl aqueous solutions at different concentrations. When pure water was intruded, a bumper behavior was exhibited with an intrusion pressure of 82 MPa and an absorbed energy of 6.6 J g−1. Changing the intruded liquid from water to LiCl aqueous solutions, an increase of the intrusion pressure was observed with 119, 175 and 280 MPa for 5 M, 10 M and 20 M LiCl aqueous solutions, respectively. The energy that the latter system could absorb (30.8 J g−1) was among the highest ever reported. A change in the behavior with LiCl concentration was also observed. The “ITH-type zeosil–20 M LiCl solution” system demonstrated a combination of bumper and shock-absorber behaviors, whereas a bumper behavior was displayed for water and the other LiCl aqueous solutions. All the zeolite samples were characterized before and after intrusion–extrusion experiments (XRD, SEM, N2 adsorption–desorption, TG and NMR analysis) in order to understand the influence of LiCl concentration on the “zeosil–liquid” system behavior.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...