Direct C–C coupling of acetone at α-position into 2,5-hexanedione induced by photochemical oxidation dehydrogenation†
Abstract
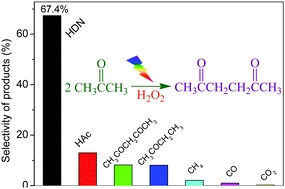
Facile carbon–carbon bond formation was achieved through the dehydrogenation coupling of acetone at the α-position. Using the H2O2/UV-light system, the acetonyl radicals that were formed from the selective cleavage of the α-C–H bond of acetone underwent a C–C coupling reaction. By modulating the instantaneous concentration of hydrogen peroxide, the direct C–C coupling of acetone was achieved. Moreover, the selectivity and generation rate of 2,5-hexanedione reached 67.4% and 8.6 mmol h−1, respectively.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...