Influence of transition metal (Fe, Co, and Ag) doping on the MnOx–CeO2/Ti-bearing blast furnace slag catalyst for selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 at low temperature
Abstract
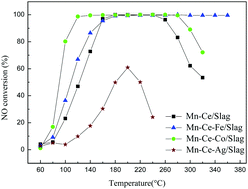
Ti-Bearing blast furnace slag has been found to be suitable as the support of the selective catalytic reduction (SCR) catalysts. Mn–Ce–M (M = Fe, Co, Ag)/Slag catalysts prepared using a solution impregnation method for the low-temperature selective catalytic reduction (SCR) of NO with NH3 under the influence of transition metals were investigated in this study. The experiments suggested that the addition of Co can greatly enhance the SCR activity and the addition of Fe can broaden the SCR temperature range (NO conversion >90%), while the addition of Ag reduced the SCR activity. The XRD and SEM analyses revealed that for the Co and Fe doped catalysts, the active components were well dispersed, while the Ag doped catalyst had agglomeration and sintering. The XPS results revealed that the Fe and Co doped catalysts had relatively higher ratios of Mn4+/Mn3+, Ce3+/Ce4+ and Oα/Oα + Oβ. TPR results showed that the redox properties were enhanced after adding Co and Fe. NH3-TPD was also studied to investigate the acid sites over the surface of the catalysts. And the addition of Co and Fe increased strong acid sites on the surface of the catalyst. However, the strength of acid sites over the surface of the Ag doped catalyst was too high to cause the desorption of NH3.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...