Reduced graphene oxide/platinum nanoparticles/nafion nanocomposite as a novel 2D electrochemical sensor for voltammetric determination of aliskiren†
Abstract
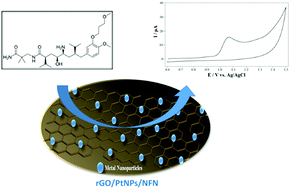
This study describes the fabrication of a sensitive and selective graphene-based electrochemical nanosensor for the detection of aliskiren (ALS). It is the first research study where the electrochemical oxidation and determination of ALS were investigated by cyclic voltammetry (CV) and adsorptive stripping differential pulse voltammetry (AdsDPV) using a 2D nanocomposite electrode modified with reduced graphene oxide/platinum nanoparticles/nafion (rGO/PtNPs/NFN/GCE). An rGO/PtNP nanocomposite was synthesized directly from graphene oxide (GO) and platinum salt using a single-step chemical reduction method. The synthesized rGO/PtNPs were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The developed sensor exhibited excellent electrocatalytic activity (i.e. shifting the potential from 1225 to 1059 mV) towards the oxidation of ALS. The voltammetric responses of ALS presented a good linearity with an increase in concentration within two concentration ranges of 0.045–0.45 μM and 0.45–2.70 μM with a low detection limit of 8.2 nM. The analytical applicability of the proposed sensor was demonstrated by determining ALS with the recovery result of 97.0% in human blood plasma. The results strongly suggested that the proposed sensor could be promising as an alternative analytical approach for routine analysis of ALS in clinical samples.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...