Effect of spacer length of ionic liquid-type imidazolium gemini surfactant-based water-in-oil microemulsion for the extraction of gold from hydrochloric acid†
Abstract
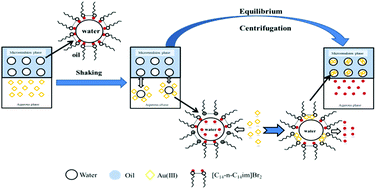
Microemulsions consisting of ionic liquid-type imidazolium gemini surfactants with different spacer lengths ([C14-n-C14im]Br2, n = 2, 4, 6), cyclohexane, n-hexyl alcohol and hydrochloric acid solution, were investigated for Au(III) extraction. [C14-n-C14im]Br2 in the microemulsion played a dual role as surfactant and extractant. The extraction efficiency (E%) of the [C14-n-C14im]Br2/cyclohexane/n-hexyl alcohol/HCl microemulsion system for Au was above 99% under optimal conditions. The results of our study indicated that the Au(III) extraction ability of the three different [C14-n-C14im]Br2 with different spacer lengths was better with longer a spacer. The mechanism for the Au(III) extraction by [C14-n-C14im]Br2 was confirmed to be based on an anion-exchange process by the continuous variation method and spectroscopic analysis (UV-Vis, FT-IR, 1H-NMR). The FT-IR spectra indicated that the better extraction ability of [C14-n-C14im]Br2 for Au(III) was positively correlated with the spacer length, due to a less significant steric effect of the methylene groups in surfactants with longer spacers. The electric conductivity values of the [C14-n-C14im]Br2 microemulsions indicated that surfactants with longer spacers can ionize to a higher extent to give more [C14-n-C14im]2+ cations and Br− anions, thus promoting anion-exchange and further increasing E%.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...