A novel hydrogel with dual temperature and pH responsiveness based on a nanostructured lipid carrier as an ophthalmic delivery system: enhanced trans-corneal permeability and bioavailability of nepafenac
Abstract
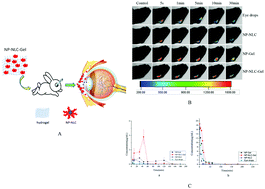
The aim of the current study was to encapsulate nepafenac (NP) in in situ hydrogel modified nanostructured lipid carrier (NP-NLC-Gel) nanoparticles as an efficient ocular delivery system to improve its transcorneal penetration and precorneal retention. NP-NLC nanoparticles were prepared by a melt emulsification method. The synthesized hydrogel, composed of poloxamer 407 and carboxymethyl chitosan, was a liquid solution at low temperature and pH and then turned to a semisolid on the surface of the cornea. The enhanced transcorneal penetration of the NLC was evaluated using isolated rabbit corneas, with a significant increase of 2.36-fold in the apparent permeability coefficient compared to that of the NP eye drops (p < 0.05). Precorneal retention assessed by fluorescence imaging technology in vivo showed that NP-NLC-Gel had a longer retention time on the corneal surface compared with the NP eye drops. The in vivo ocular tolerance study indicated that there was no difference in irritation between the NP eye drops and NP-NLC-Gel. The concentration of nepafenac in the aqueous humor and lacrimal fluid was determined using HPLC. The AUC0−∞ of NP-NLC-Gel was increased up to 6.3- and 1.9-fold in the aqueous humor and lacrimal fluid, respectively, as compared with the eye drops. In conclusion, NP-NLC-Gel possesses a greater potential as an ocular drug delivery system compared with the NP eye drops.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...