Fe/C and FeMo/C hybrid materials for the biphasic oxidation of fuel contaminants
Abstract
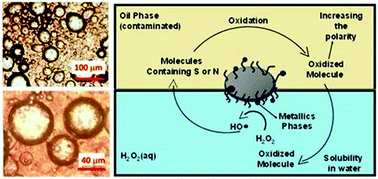
In the present work, hybrid magnetic nanoparticles based on Fe and FeMo coated with carbon nanostructures (Fe/C and FeMo/C) were produced by catalytic chemical vapor deposition at different temperatures using ethanol as the carbon source. Scanning electron microscopy, thermal analysis, Raman spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, and Mössbauer spectroscopy analyses suggested that hematite was reduced by ethanol at 700 and 900 °C, producing carbon nanostructures such as nanofibers and nanotubes. The Fe/C and FeMo/C hybrid composites showed remarkable magnetic and amphiphilic properties. The composites were successfully used to oxidize sulfur and nitrogen contaminants present in fuels in a biphasic system.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...