The synthesis and characterization of tributyl phosphate grafted carbon nanotubes by the floating catalytic chemical vapor deposition method and their sorption behavior towards uranium
Abstract
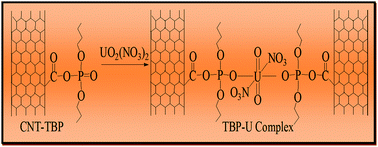
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) were synthesized by the floating catalytic chemical vapor deposition technique using ferrocene in benzene as the hydrocarbon source. The functionalization of CNTs was carried out by oxidation (CNT-OX) and grafting with a tributyl phosphate (TBP) ligand (CNT-TBP). Various spectroscopic techniques including scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Fourier Transform Infra Red Spectroscopy (FTIR), BET surface area and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) were used to characterize the adsorbents. FTIR and XPS studies revealed the efficient grafting of the TBP ligand on the CNT surface. The effect of the initial pH and the contact time for the maximum adsorption of U(VI) with CNT-plain, CNT-OX and CNT-TBP was studied. The spontaneity of the sorption was confirmed by thermodynamic data. A pseudo second order model with a regression coefficient of >0.978 was obtained for CNT-TBP and equilibrium was reached within 3 h. The Langmuir maximum adsorption capacity of U(VI) at pH 5 for CNT, CNT-OX and CNT-TBP was found to be 66.6, 100.0 and 166.6 mg g−1 respectively. Using 0.1 M HCL as a desorbent, recyclability studies were carried out for three cycles. The probable mechanism of adsorption between U(VI) and CNT-TBP could be understood through FTIR and XPS techniques.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...