Development of a Fe3O4@SnO2:Er3+,Yb3+–APTES nanocarrier for microwave-triggered controllable drug release, and the study of the loading and release mechanisms using microcalorimetry
Abstract
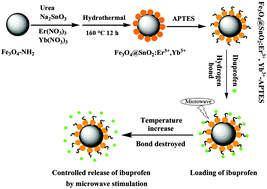
We fabricated an efficient microwave-triggered controlled-release nanocarrier system using Fe3O4@SnO2:Er3+,Yb3+–APTES multifunctional core–shell nanoparticles. We also studied the drug loading and release mechanisms by means of microcalorimetry. The thermodynamic parameter values for loading (ΔH = −42.64 kJ mol−1, ΔS = −452.98 J mol−1 K−1) showed that the main interaction between the nanocarrier and drug molecules is relatively weak hydrogen bonding. The molar enthalpy (ΔH) of the drug-release process was 10.30 kJ mol−1, which indicates an endothermic process. This suggests that drug release can be controlled by microwave heating. When energy provided from the medium rises above the hydrogen bond energy, the hydrogen bond breaks and the nanocarrier begins to release the drug. The release profile can be controlled by the duration and number of cycles of microwave application. Approximately 71% of ibuprofen was released after four cycles. The microwave-stimulated, thermally sensitive, multifunctional nanoparticles therefore represent a new system with potential utility for on-command drug release, and the fluorescence properties allow in situ monitoring.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...