Superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles: synthesis by a solvothermal process and functionalization for a magnetic targeted curcumin delivery system
Abstract
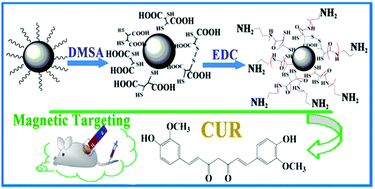
Tailoring surface characteristics is necessary for the biomedical application of superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles. This study developed an approach for the synthesis of Fe3O4 nanoparticles with different functional groups grasped on the surface and the influence of different functionalization on the behavior of drug loading and release was also assessed. Monodisperse Fe3O4 nanoparticles were first prepared through a novel and simplified solvothermal process. The resulting oleylamine coated nanoparticles (about 4.3 nm in diameter) were carboxylated by meso-2,3-dimercaptosuccinic acid (DMSA) ligand-exchange reactions and further development of amino-functionalized nanoparticles (Fe3O4@DMSA–NH2 NPs) was achieved by chemical reaction with a short chain molecule ethanediamine via 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-carbodiimide hydrochloride activation of the carboxylic acids on the surface of DMSA-coated Fe3O4 NPs. The two types of functionalized magnetic nanoparticles with –COOH and/or –NH2 fabricating their hydrophilicity were characterized and designed as drug carriers to load a natural antitumor drug, curcumin (CUR), which is water-insoluble and instable. The loading process could be described by the Langmuir adsorption isothermal model and pseudo-second-order kinetic model for both functionalized Fe3O4 NPs and a stronger drug-loading ability was observed from the Fe3O4@DMSA–NH2 NPs. Furthermore, it's worth noting that all the particles showed a relatively pH-sensitive drug release and the Fe3O4@DMSA–NH2 NPs showed a prolonged drug release, which makes them suitable for use as a scaffold for the design of a pH-sensitive based controlled release carrier. Due to those properties, the functionalized nanoparticles have great promise to be developed as a magnetic targeted drug delivery system for hydrophobic drugs.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...