Molecular structure, spectral analysis and hydrogen bonding analysis of ampicillin trihydrate: a combined DFT and AIM approach†
Abstract
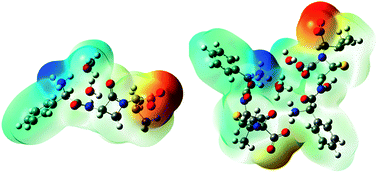
Ampicillin trihydrate chemically associated with the empirical formula C16H19N3O4S·3H2O, is a semi-synthetic amino-penicillin derived from the elementary penicillin nucleus, 6-aminopenicillanic acid. It is a very common antibiotic that is active against an extensive range of Gram-positive and Gram-negative organisms. It is used to treat certain varieties of bacterial infections, like gonorrhea and infections of the urinary, intestinal and respiratory tracts. In the present effort, quantum chemical calculations of molecular geometries (bond lengths and bond angles) and bonding features of the monomer and dimer of ampicillin trihydrate in the ground state have been carried out due to its biological and industrial importance. The optimized geometry and wavenumber of the vibrational bands of the molecule have been calculated by ab initio density functional theory (DFT) using Becke's three-parameter hybrid functional (B3LYP) with a 6-311++G(d,p) basis set. Vibrational wavenumbers were compared with the observed FT-Raman and FT-IR spectra. Molecular electrostatic potential (MEP) has also been plotted for predicting the molecule reactivity towards positively or negatively charged reactants and it shows that electropositive potential is visualized in the vicinity of the –NH3+ group and the electropositive region is found near the H2O molecule in both monomer and dimer. HOMO–LUMO analysis has been done to describe the way the molecule interacts with other species. Natural bond orbital (NBO) analysis has been carried out to inspect the intra- and inter-molecular hydrogen-bonding, conjugative and hyperconjugative interactions and their second order stabilization energy E(2). Nonlinear optical (NLO) analysis has also been performed to study the non-linear optical properties of the molecule by computing the first hyperpolarizability (β0). The variation of thermodynamic properties with temperature has been studied. Topological parameters at bond critical points (BCP) have been evaluated by ‘Quantum theory of atoms in molecules’ (QTAIM).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...