Mechanistic studies on the pH-controllable interconversion between hydrogen and formic acid in water: DFT insights†
Abstract
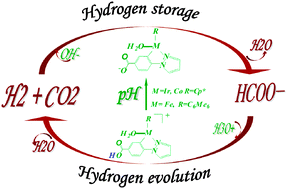
A complete reaction mechanism for interconversion between hydrogen and formic acid catalyzed by [C,N] cyclometallated organoiridium complex [IrIII(Cp*)(4-(1H-pyrazol-1-yl-κN2)benzoic acid-κC3)(H2O)]2·SO4, i.e. [Ir-1]2·SO4, has been revealed by density functional theory (DFT) calculations. For both the hydrogen storage catalytic cycle I and hydrogen evolution catalytic cycle II, the detailed reaction profiles with the key transition states and intermediates are revealed. Catalytic cycle I shows that the dihydrogen heterolysis facilitated by OH− gives the considerable stable iridium hydride intermediate M-4, followed by an outer-sphere hydrogen transfer to afford a metal–formate complex M-6. Upon the increasing of pH, catalytic cycle II occurs via the generation of the metal–formate complex M-7, followed by the outer-sphere β-H elimination to form a metal–hydride complex M-9, which is subsequently protonated by the hydrated proton H3O+ to afford dihydrogen. The decomposition of bicarbonate and the β-hydride elimination of formate are believed to be the rate-determining steps for cycle I and II, respectively. The acid–base equilibrium between the hydroxy and oxyanion form on the catalyst [C,N] ligand has a considerable influence on the catalytic hydrogen transfer. Our studies are in good agreement with experimental results. Remarkably, the new theoretically designed low-cost cobalt(III) complex, as a promising catalyst, exhibits catalytic activity for the interconversion between hydrogen and formic acid.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...