Chemical fixation of CO2 into cyclic carbonates by azo-containing Schiff base metal complexes†
Abstract
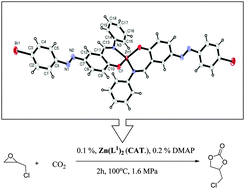
Two new ligands containing a –N![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N– group, 4-((E)-(4-bromophenyl)diazenyl)-2-((E)-(phenylimino)methyl)phenol (L1H, 2), 4-((E)-(4-bromophenyl)diazenyl)-2-((E)-((4-ethylphenyl)imino)methyl)phenol (L2H, 3) and their metal complexes were synthesized. The synthesized metal complexes were used as catalysts for the chemical fixation of CO2 into cyclic carbonates using epoxides which were used as both substrate and solvent. According to analytical, UV-visible and IR data, the metal complexes are formed by coordination of the N and O atoms of the ligands and the metal : ligand ratio was found to be 1 : 2 for all the complexes. The TG and DTA results showed that these complexes had good thermal stability. The molecular structures of ligand 2 (L1H) and its ZnII complex 4 (Zn(L1)2) were determined by single crystal X-ray diffraction studies. After choosing the most active catalyst (Zn(L1)2, 4), optimization studies were performed by changing various parameters. Ionic liquids have been found to have a positive effect and showed the most active performance with (bmim)PF6 + Zn(L1)2 (4) as a binary catalytic system.
N– group, 4-((E)-(4-bromophenyl)diazenyl)-2-((E)-(phenylimino)methyl)phenol (L1H, 2), 4-((E)-(4-bromophenyl)diazenyl)-2-((E)-((4-ethylphenyl)imino)methyl)phenol (L2H, 3) and their metal complexes were synthesized. The synthesized metal complexes were used as catalysts for the chemical fixation of CO2 into cyclic carbonates using epoxides which were used as both substrate and solvent. According to analytical, UV-visible and IR data, the metal complexes are formed by coordination of the N and O atoms of the ligands and the metal : ligand ratio was found to be 1 : 2 for all the complexes. The TG and DTA results showed that these complexes had good thermal stability. The molecular structures of ligand 2 (L1H) and its ZnII complex 4 (Zn(L1)2) were determined by single crystal X-ray diffraction studies. After choosing the most active catalyst (Zn(L1)2, 4), optimization studies were performed by changing various parameters. Ionic liquids have been found to have a positive effect and showed the most active performance with (bmim)PF6 + Zn(L1)2 (4) as a binary catalytic system.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...