A highly dispersible silica pH nanosensor with expanded measurement ranges†
Abstract
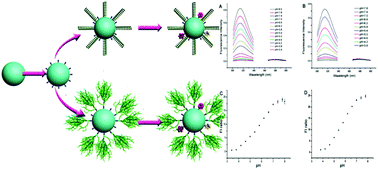
For accurate determination of local intracellular pH which could further improve our understanding of cellular processes and knowledge of advanced drug delivery system architecture, a fluorescent-based ratiometric nanosensor has been designed over the past decade. As a promising matrix for nanosensors and nanomedicines, silica nanoparticles (SNPs) have been widely used due to their desirable properties, which include a high loading level of guest molecules, low toxicity and easy functionalization. Amination of SNPs was essential for binding functional groups, such as fluorescent molecules and targeting groups, whereas positively charged amine will cause the aggregation of SNPs which limits the further application of SNPs. To circumvent this problem, a simple and effective strategy has been presented in this paper. Firstly, an acid was used as a catalyst instead of a base to inhibit SNP aggregation in the amination process. Subsequently, polymers (poly(ethylene glycol) and hyaluronic acid) were coated on the surface of monodispersed aminated SNPs to obtain excellent colloidal stability. The well dispersed core–shell SNPs were further functionalized with two pH sensitive fluorophores (fluorescein isothiocyanate and Oregon Green isothiocyanate) and one reference fluorophore (rhodamine B isothiocyanate), which resulted in ratiometric pH nanosensors with a hydrodynamic diameter of 76–100 nm. The sensors exhibited a broad pH measurement range from 3.8 to 7.4, which covers almost all intracellular pH values, and remarkable colloidal stability in buffer solution.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...